Liver
Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is an infection mainly affecting the liver and is typically transmitted through contact with the blood from an infected individual. It’s usually contracted by sharing needles, exposure to infected blood via transfusions or through unprotected sexual activity with a person carrying the virus. Quite a lot of individuals with Hepatitis C don’t manifest any symptoms at the early stages, making its detection quite challenging. Yet, as the infection takes hold, noticeable symptoms like fatigue, jaundice, and abdominal discomfort might develop. Hepatitis C detection involves a blood examination to verify the virus’s presence. If the infection is confirmed, several treatments can be utilized, inclusive of antiviral drugs to assist in eliminating the virus from the body. Regular health checks are crucial to gauge the effectiveness of the treatment and ward off complications such as liver deterioration or cirrhosis.
Transmission and Risk Factors

Hepatitis C is mainly spread via contact with an infected individual’s blood. Primary paths of transmission consist of needle sharing among drug users, receiving tainted blood through organ transplants or transfusions, and accidental needle pricks in medical settings. The virus’s sexual transmission is possible, but the risk remains relatively low. A past of injection drug usage, undergoing lengthy dialysis treatment, birth from a Hepatitis C positive mother, and receiving tattoos or piercings with unsterilized equipment are among other Hepatitis C risk factors. It’s crucial to stress that casual contact, such as sharing meals or drinks, or through forms of affection like hugging or kissing, does not transmit Hepatitis C.
Symptoms and Progression
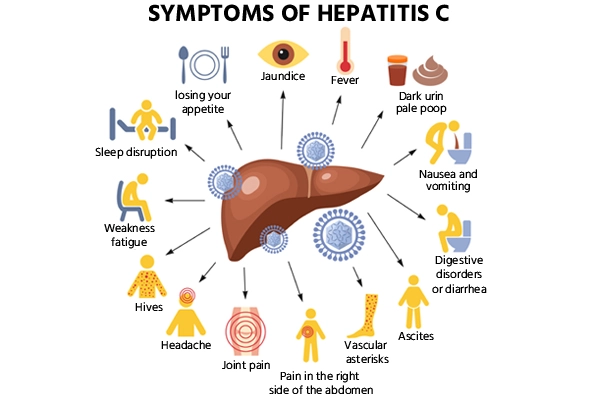
Hepatitis C manifestations can range in severity from light to potent and might not become evident until several years post infection. Usual symptoms encompass feeling of fatigue, symptoms akin to flu, pain in the abdomen, and sensations of nausea. As the ailment advances, symptoms intensify and might feature jaundice, unusually darkened urine, and edema in the legs and abdomen. Hepatitis C, in particular instances, can trigger inflammation and scarring of the liver, a condition termed as cirrhosis, which can precipitate grave complications. If any of these symptoms manifest, it is prudent to seek prompt medical intervention as early identification and remedial measures can enhance prognosis and thwart additional damage to the liver.
Testing and Diagnosis

The importance of testing and diagnosing in the management of hepatitis C cannot be overstated. There are a variety of tests that can be employed to verify if a person harbors the virus. Among these are blood examinations looking for hepatitis C antibodies. If these antibodies are found, further tests are conducted to ascertain the viral load in the blood, the viral genotype, and the degree of injury to the liver. These diagnostic procedures provide healthcare professionals with the necessary info to understand the disease’s advancement and create a fitting treatment strategy. Those at a heightened risk or exhibiting symptoms of hepatitis C should proactively seek testing as early detection and action can enhance results and prevent additional liver harm. Frequent screenings are likewise advocated for those with prominent risk contributions like injectable drug use or a background of blood infusions. In a nutshell, the role of testing and diagnosis is vital in the governance of hepatitis C and guarantees that the correct treatment is administered.
Treatment Options
There are various treatments available for hepatitis, and the chosen method depends on the kind and severity of the infection. For conditions such as chronic hepatitis B and C, antiviral drugs are commonly used. These medications assist in diminishing the viral load in the patient’s body, slowing the progression of liver damage, and enhancing liver functionality. Advanced liver disease may require a liver transplant in certain scenarios. When it comes to hepatitis A, the treatment plan is largely supportive, aiming to manage symptoms and avert complications. Recommendations typically include rest, staying hydrated, and steering clear of alcohol and specific medications. Vaccines for hepatitis A and B are available and act as a vital preventive measure against infection. Consulting a health practitioner for an accurate diagnosis and suitable treatment plan for hepatitis is critical.